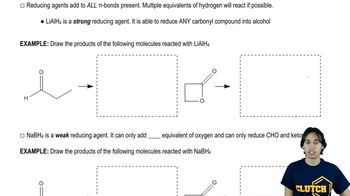
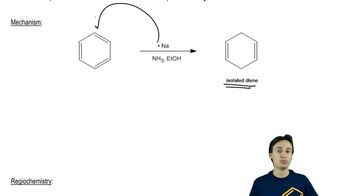
Predict the products you would expect from the reaction of LiAlH4 followed by hydrolysis with the following compounds. You may assume that these reactions take place in methanol as the solvent.
(d)
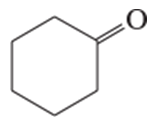
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: