For each set of reactive intermediates, rank them in order of reactivity (1 = most reactive).
(b)
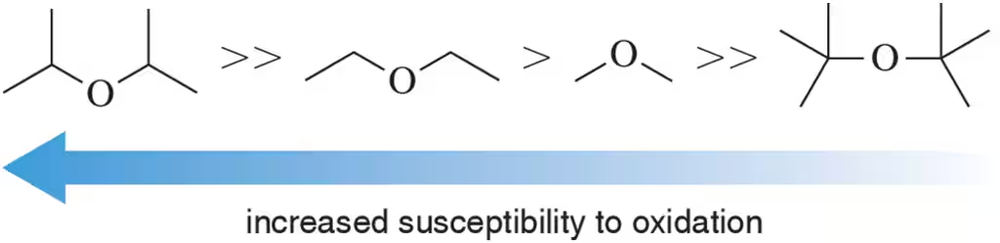
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 3:43m
3:43mMaster The radical stability trend. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning