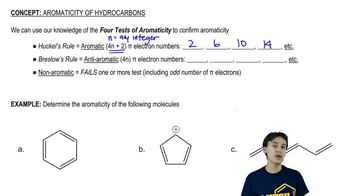
Predict the product of each of the following hydroboration–oxidation or oxymercuration–reduction reactions used in the modern synthetic organic chemistry literature (modified to use reagents we are used to seeing).
(c) A similar sequence was featured in the synthesis of muricadienin, a proposed precursor in the biosynthesis of solamin (Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5886–5889).