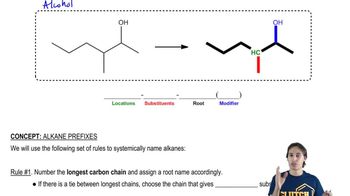
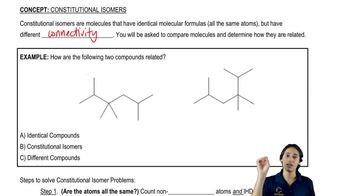
A student was given the structural formulas of several compounds and was asked to give them systematic names. How many did the student name correctly? Correct those that are misnamed.
c. 5-methylcyclohexanol
d. 1,1-dimethyl-2-cyclohexanol
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: