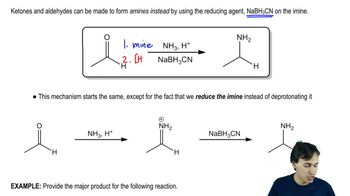
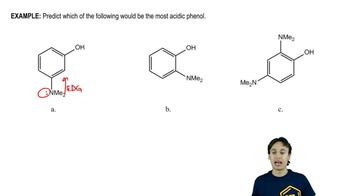
Compounds containing deuterium (D = 2H) are useful for kinetic studies and metabolic studies with new pharmaceuticals. One way to introduce deuterium is by using the reagent LiAlD4, equivalent in reactivity to LiAlH4. Show how to make these deuterium-labeled compounds, using LiAlD4 and D2O as your sources of deuterium, and any non-deuterated starting materials you wish.
(b) CH3CD2OH