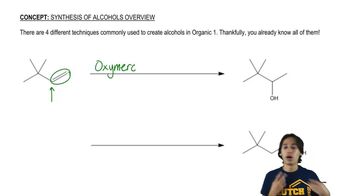
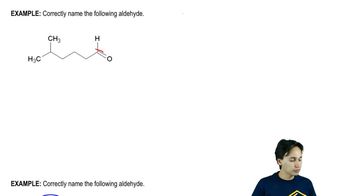
Show how you would synthesize each compound, starting with an ester containing no more than eight carbon atoms. Any other necessary reagents may be used.
(d) Ph2CHOH
(e) PhCH2OH
(f) PhCOOH
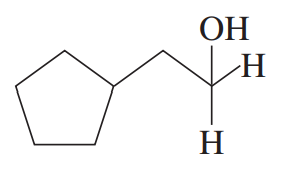
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: