Provide the alcohol that would be used to make the bromoalkanes shown using PBr₃.
(c)
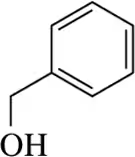
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: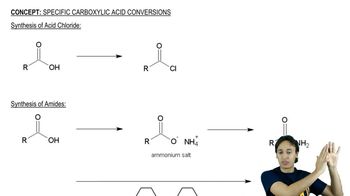

 7:18m
7:18mMaster Learning the mechanism of SOCl2. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning