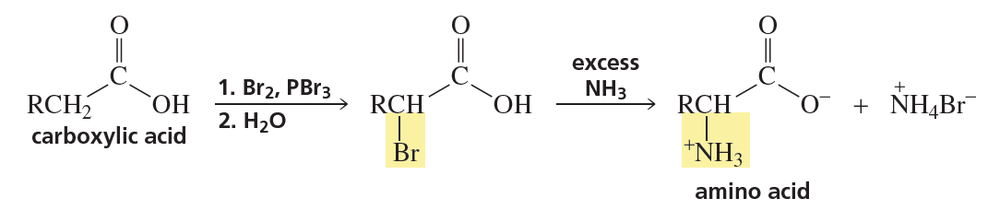
Indicate the peptides produced from cleavage by the indicated reagent:
a. His-Lys-Leu-Val-Glu-Pro-Arg-Ala-Gly-Ala by trypsin
b. Leu-Gly-Ser-Met-Phe-Pro-Tyr-Gly-Val by chymotrypsin
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 9:34m
9:34mMaster Peptides and Polypeptides with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning