Suppose you intend to synthesize the secondary alkyl halide from each reaction shown.
(b) What is the E-factor, effective mass yield, and process mass intensity?
(c) Which reaction would you consider greener? Why?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: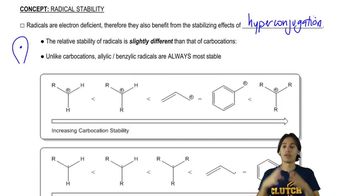
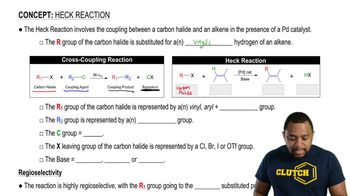
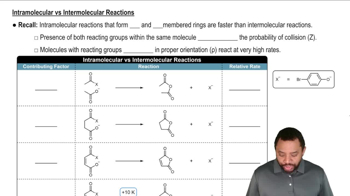

 4:32m
4:32mMaster Explaining relative rates of halogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning