For each reaction, estimate whether ΔS° for the reaction is positive, negative, or impossible to predict.
(c)
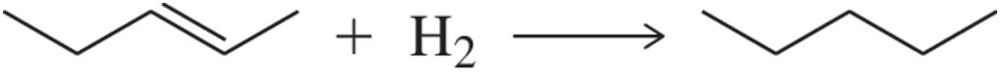
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:46m
2:46mMaster Explaining what entropy is. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning