α-Amino acids can be prepared by treating an aldehyde with ammonia/trace acid, followed by hydrogen cyanide, followed by acid-catalyzed hydrolysis.
a. Draw the structures of the two intermediates formed in this reaction.
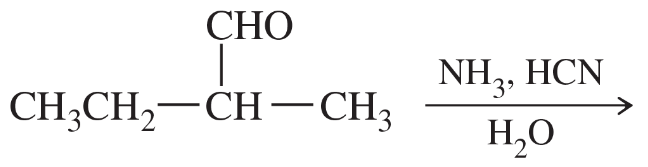
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 9:34m
9:34mMaster Peptides and Polypeptides with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning