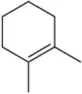
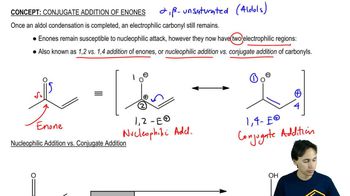
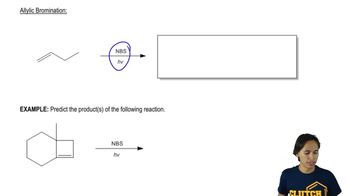
Using 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.) If a chiral product is shown, assume that it is part of a racemic mixture.
(c)