Open Question
Outline the synthetic pathway for the creation of p-dimethylaminoacetophenone from bromobenzene.
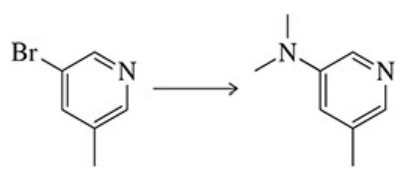
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: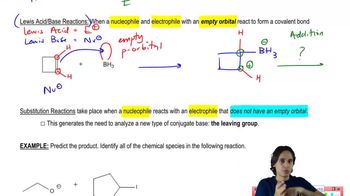
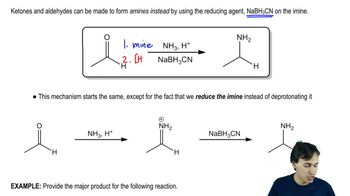
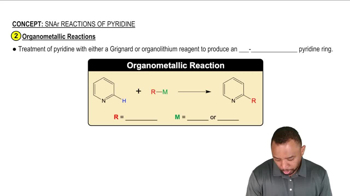

 3:46m
3:46mMaster Buchwald-Hartwig Amination Reaction with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning