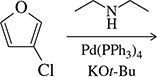
Textbook Question
Suggest reagents to carry out the following transformations. Some may require more than one step.
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 3:46m
3:46mMaster Buchwald-Hartwig Amination Reaction with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning