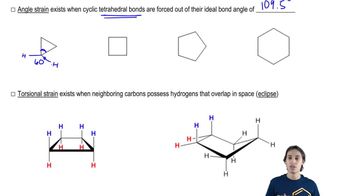
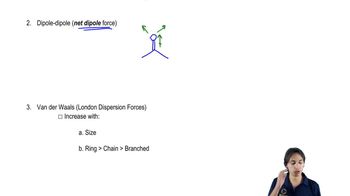
Use the symbols δ+ and δ− to show the direction of the polarity of the indicated bond in each of the following compounds:
c. H3C—NH2
d. H3C—Cl
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: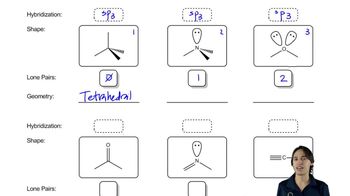

 11:33m
11:33mMaster Differences between ionic, polar and covalent bonds with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning