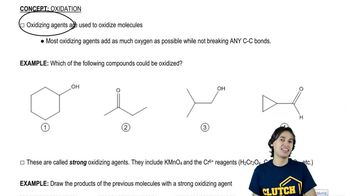
Predict the major products formed when the following amines undergo exhaustive methylation, treatment with Ag2O, and heating.
(a) hexan-2-amine
(b) 2-methylpiperidine
(c) N-ethylpiperidine
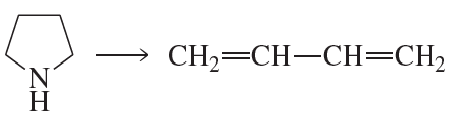
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: