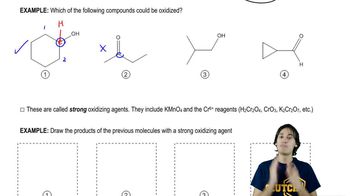
Determine the oxidation number of each carbon indicated by an arrow.
(e)
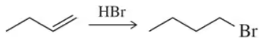
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: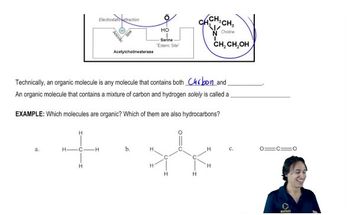


 6:02m
6:02mMaster General Features of Redox with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning