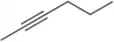
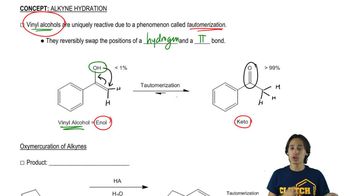
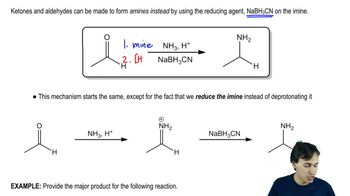
The following reaction was recently reported to have been performed electrochemically.
(a) Identify the reagent and a solvent that could have been used if this reaction was done traditionally.
(b) What safety and environmental hazards are improved or worsened when doing this reaction electrochemically?