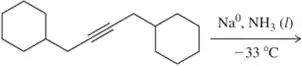
For the alkynes shows here, show the product(s) expected to form when treated under the following conditions: (ii) H2, Pd/C, Pb(OAc)2 , CaCO3 (Lindlar's catalyst). If you expect two products, show both.
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: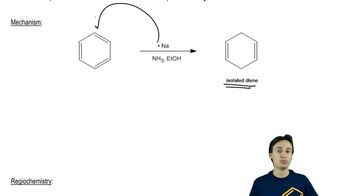
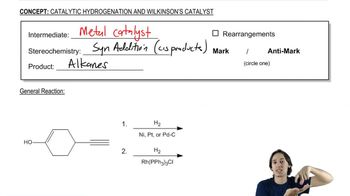
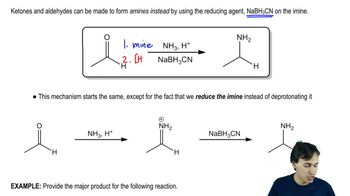

 0:48m
0:48mMaster The definition of hydrogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning