b. Using arrows, show the electron rearrangement that takes place in each reaction.
1.
2.
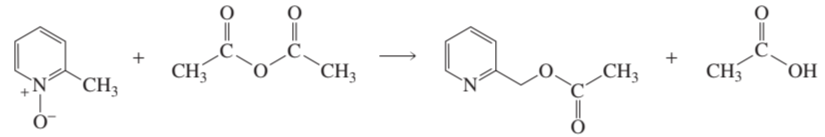
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 3:51m
3:51mMaster Definition of Sigmatropic Shifts with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning