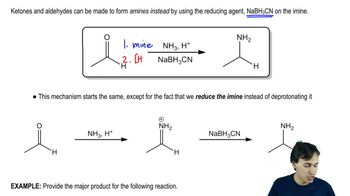
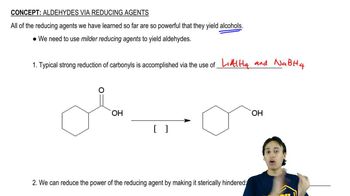
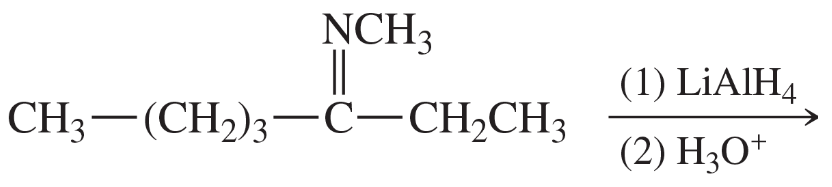Several additional amine syntheses are effectively limited to making primary amines. The reduction of azides and nitro compounds and the Gabriel synthesis leave the carbon chain unchanged. Formation and reduction of a nitrile adds one carbon atom. Show how these amine syntheses can be used for the following conversions.
(c) 1-bromo-3-phenylheptane → 3-phenylheptan-1-amine