Starting with cyclohexene, how can the following compounds be prepared?
b. cyclohexylmethylamine
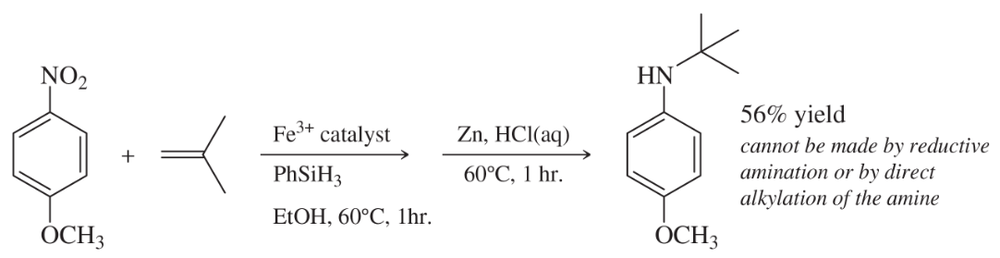
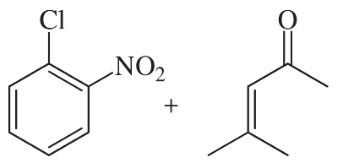
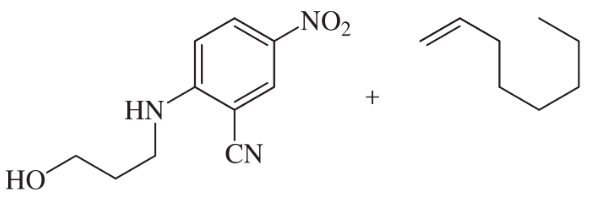
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: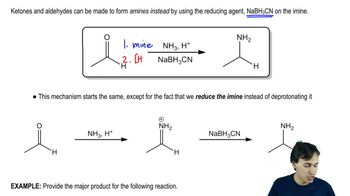
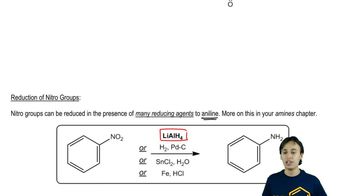
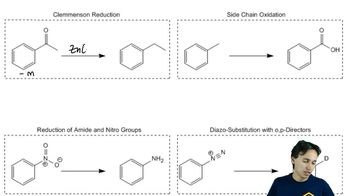

 9:12m
9:12mMaster The Primary Amines Flowchart with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning