Use bond-dissociation enthalpies (Table 4-2, p. 167) to calculate values of ΔH° for the following reactions.
d. CH3CH2CH3 + H2 → CH3CH3 + CH4
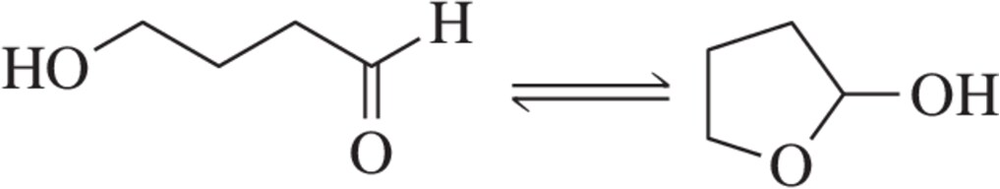
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:09m
4:09mMaster How to calculate enthalpy using bond dissociation energies. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning