Draw the ground-state electronic configuration for each of the following:
b. Ca2+
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
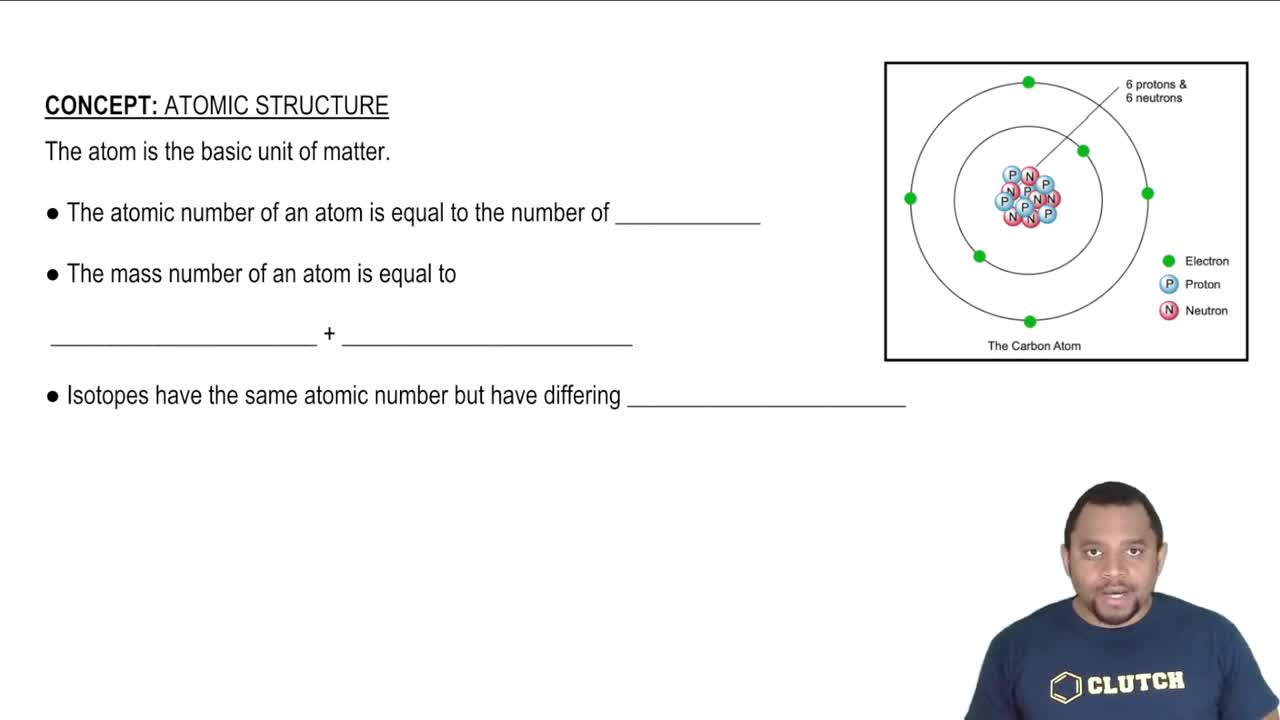

 1:44m
1:44mMaster The difference between atomic numbers and atomic mass. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning