Parts (a)–(f) of this assessment refer to the rotation around the single bond of ethane.
(c) Write the rate law for this reaction.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: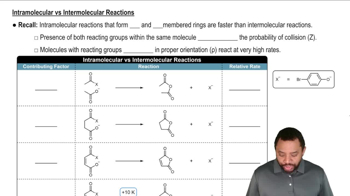
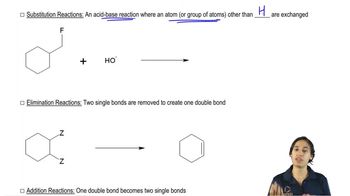
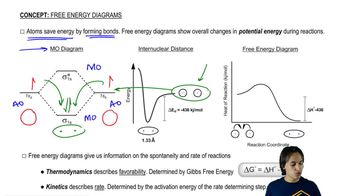

 6:07m
6:07mMaster Introduction to free energy diagrams. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning