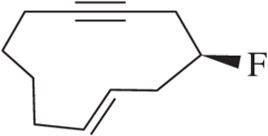
Write structural formulas for the following compounds (includes both old- and new-style names).
(j) vinylacetylene
(k) (S)-3-methyl-1-penten-4-yne
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:48m
1:48mMaster Why stereoisomers need their own naming system. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning