Textbook Question
Each of the following descriptions applies to more than one alkane. In each case, draw and name two structures that match the description.
f. a bicyclononane
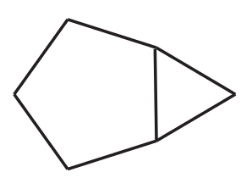
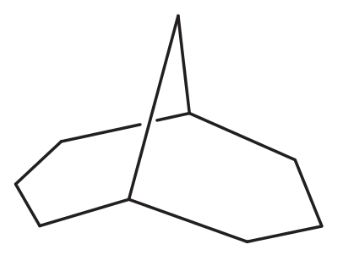
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 1:55m
1:55mMaster The two types of bicyclic molecules with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning