Show how you might use olefin metathesis to assemble the following alkenes from smaller units:
(a)
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: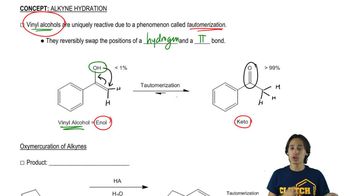
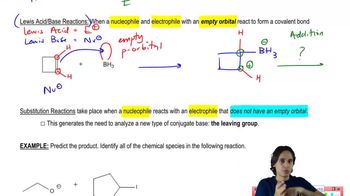


 5:39m
5:39mMaster Features of Addition Mechanisms. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning