What monosaccharide is reduced to two alditols, one of which is the alditol obtained from the reduction of
1. D-talose?
2. D-allose?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: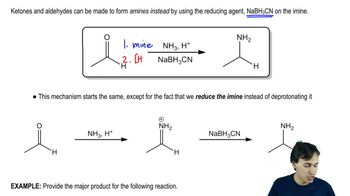
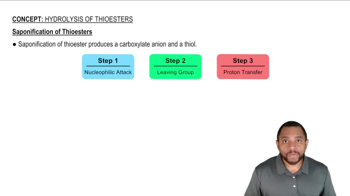
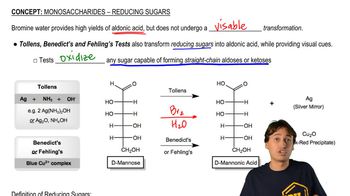

 7:19m
7:19mMaster Monosaccharides - Reduction (Alditols) with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning