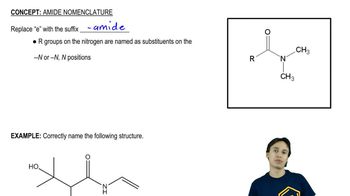
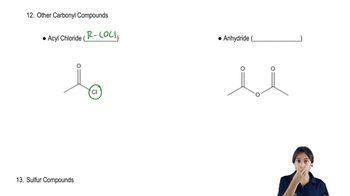
Which alkyl halides form the carboxylic acids listed here after reaction with sodium cyanide followed by heating the product in an acidic aqueous solution?
a. butyric acid
b. isovaleric acid
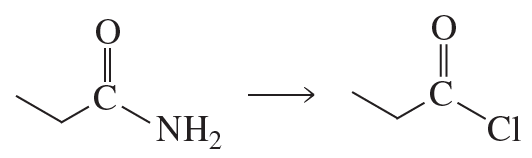
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: