Two resonance structures are shown for each molecule. Use the arrow-pushing formalism to represent the electron flow from the structure on the left to the one on the right.
(e)
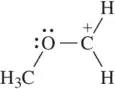
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: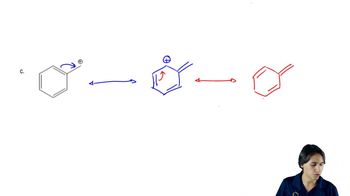

 3:34m
3:34mMaster The rules you need for resonance: with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning