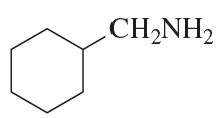
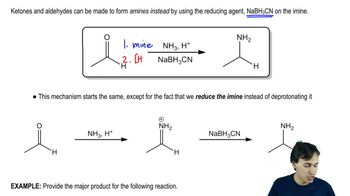
Show how you can synthesize the following compounds starting with benzene, toluene, and alcohols containing no more than four carbon atoms as your organic starting materials. Assume that para is the major product (and separable from ortho) in ortho, para mixtures.
(d) N-benzylpropan-1-amine