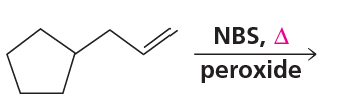
In the following allylic radicals, identify the carbon where the new C― Br bond is most likely to form in the second propagation step.
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: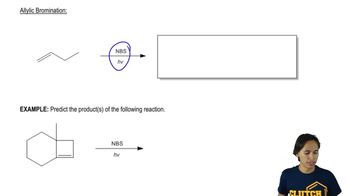
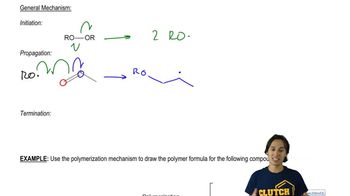

 6:15m
6:15mMaster The general mechanism of Allylic Halogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning