Draw the enol tautomers for each of the following compounds. For compounds that have more than one enol tautomer, indicate the one that is more stable.
f.
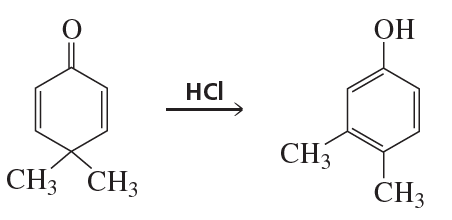
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: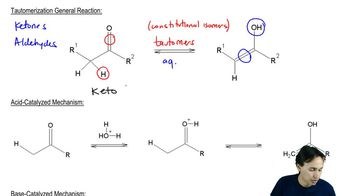
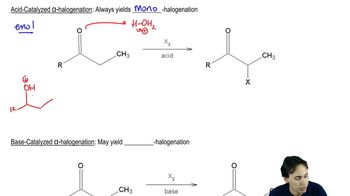


 1:51m
1:51mMaster Unusual Acidity of the Alpha Carbon with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning