Show what products you would expect from the following metathesis reactions, using the Schrock or Grubbs catalysts.
(b)
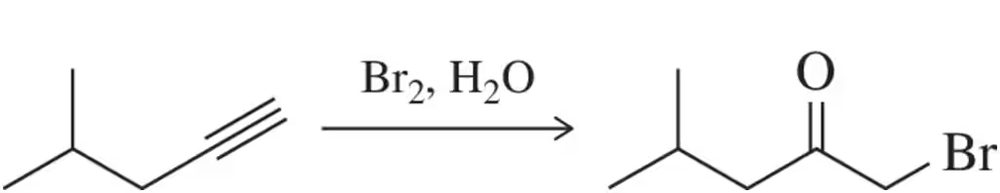
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: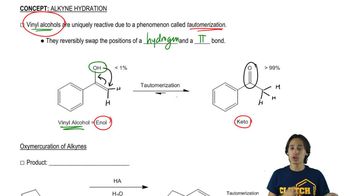


 2:15m
2:15mMaster Double halogenation of alkynes. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning