Suggest a series of steps involving a cuprate reagent that would convert the reactant on the left to the product on the right. The ideal number of steps is shown.
(a)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: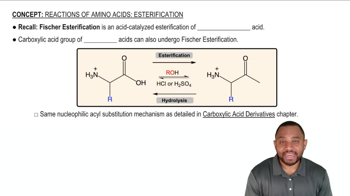
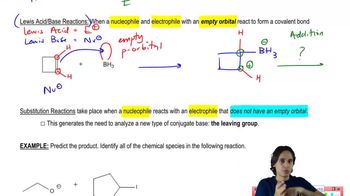


 1:36m
1:36mMaster Synthesis of Acid Chlorides with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning