Draw the structure of the activated benzene ring and the diazonium ion used in the synthesis of each of the following compounds, whose structures can be found on page 607.
b. methyl orange
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: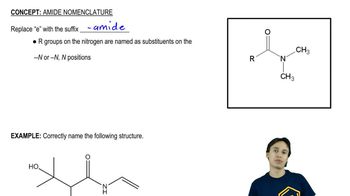

 0:43m
0:43mMaster Proposing Aromatic Synthesis with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning