Show the ionic compound that you would expect to form between the given metal and nonmetal. Label the charges on each species.
(b) Mg and Br
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: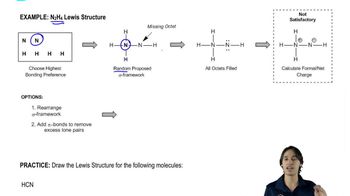
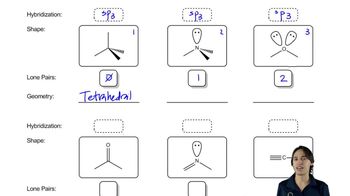
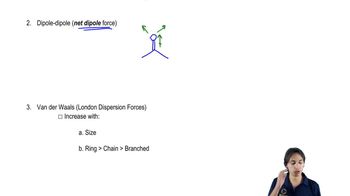

 11:33m
11:33mMaster Differences between ionic, polar and covalent bonds with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning