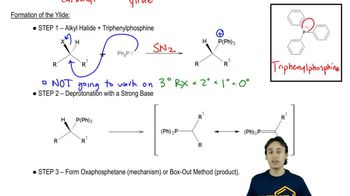
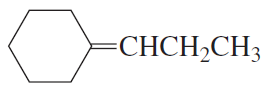Like other strong nucleophiles, triphenylphosphine attacks and opens epoxides. The initial product (a betaine) quickly cyclizes to an oxaphosphetane that collapses to an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide.
(a) Show each step in the reaction of trans-2,3-epoxybutane with triphenylphosphine to give but-2-ene. What is the stereochemistry of the double bond in the product?