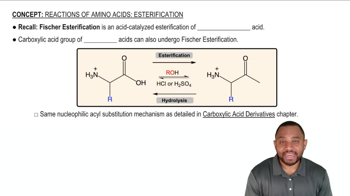
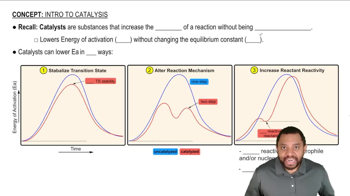
Acid-catalyzed transesterification:
Complete the mechanism for this acid-catalyzed transesterification by drawing out all the individual steps. Draw the important resonance contributors for each resonance-stabilized intermediate.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: