Propose mechanisms for the following reactions. Additional products may be formed, but your mechanism only needs to explain the products shown.
(c)
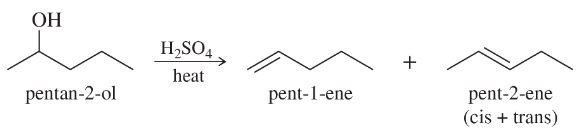
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 6:01m
6:01mMaster General features of acid-catalyzed dehydration. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning