Show how m-toluidine can be converted to the following compounds, using any necessary reagents.
(a)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: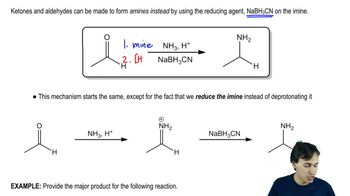
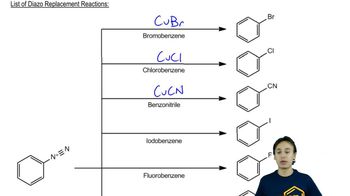

 7:11m
7:11mMaster Four Ways to Make a Primary Amine Precursor with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning