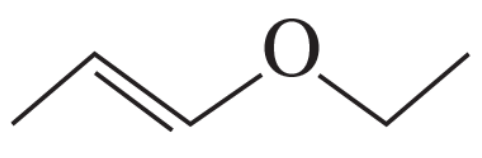
What are the major products obtained when each of the following ethers is heated with one equivalent of HI?
c.
d.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:22m
4:22mMaster How to predict the products of Ether Cleavage. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning