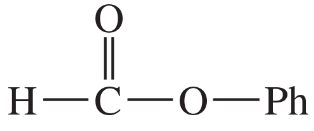Suppose we have some optically pure (R)-2-butyl acetate that has been 'labeled' with the heavy 18O isotope at one oxygen atom as shown.
(a) Draw a mechanism for the hydrolysis of this compound under basic conditions. Predict which of the products will contain the 18O label. Also predict whether the butan-2-ol product will be pure (R), pure (S), or racemized.