Using cyclooctyne as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.)
(h)
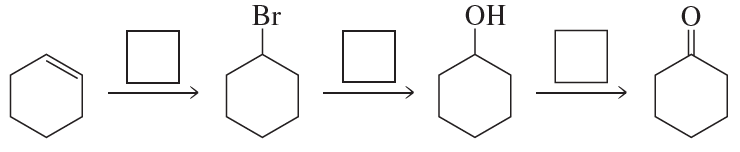
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: