Show the resonance forms for the enolate ions that result when the following compounds are treated with a strong base.
(a) ethyl acetoacetate
(b) pentane-2,4-dione
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: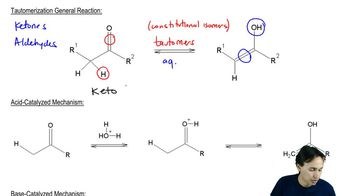
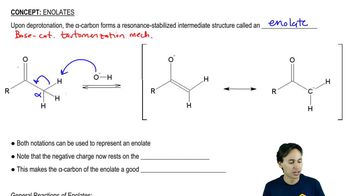
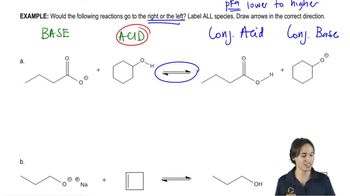

 2:26m
2:26mMaster Formation of Enolates with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning