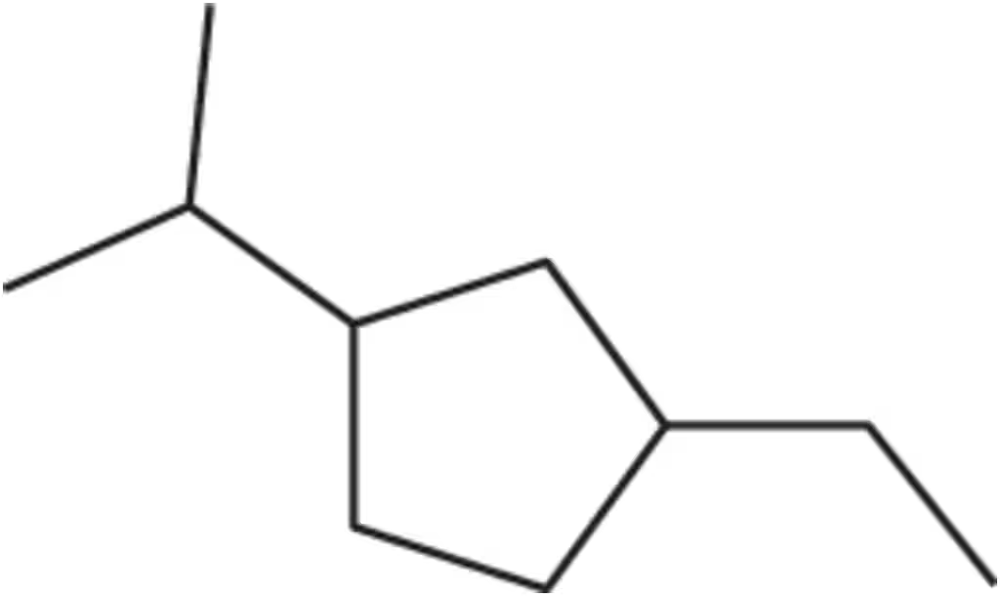
Draw the four stereoisomers of 1,3-dichloro-2-pentanol using
b. perspective formulas.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 3:51m
3:51mMaster Determining when molecules are different. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning