Identify
5. achiral compounds
6. meso compounds
7. enantiomers
8. diastereomers
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: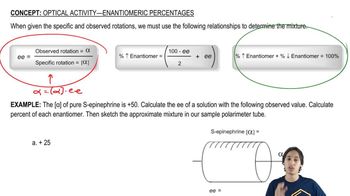


 1:41m
1:41mMaster Different atoms or different connectivity. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning