Calculate the energy difference between each pair of conformations shown by drawing and comparing Newman projections down the indicated bonds in each.
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: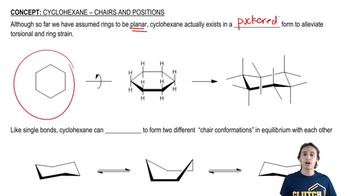


 9:55m
9:55mMaster Explaining how A-Values are related to cyclohexane flip energy with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning