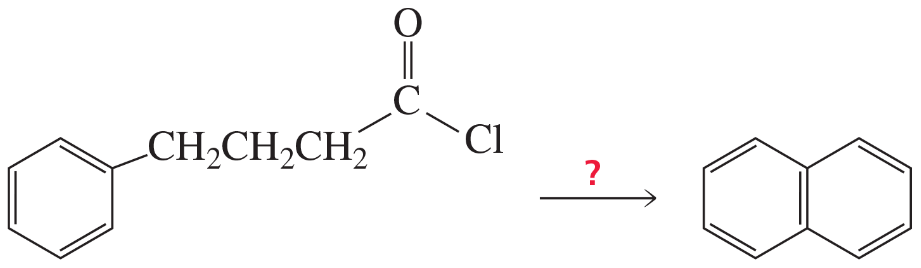
How can you prepare the following compounds with benzene as one of the starting materials?
c.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:49m
2:49mMaster Aromatic synthesis starting with benzene/benzene derivatives with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning